Energy trends show sustainable development in renewables
Written by Lewis Morgan
Posted on October 10, 2014
Latest figures from the Department of Energy and Climate Change reveal a positive picture in the development of sustainable energy sources from renewables.
That’s good news for the planet, along with the indications that overall UK domestic electricity consumption is shrinking. This is a combination of more efficient household appliances and behavioural changes.
We think that the reduction curve can be accelerated simply by a national supported programme to encourage and fund the replacement of energy-guzzling traditional light bulbs with LED lighting that cuts electricity consumption by up to 85%.
The DECC data shows that the share of renewables (hydro, wind and other renewables) increased from 15.9 per cent in 2013 Q2 to 16.8 per cent in 2014 Q2. This was due to increased hydro generation as well as the conversion of the Drax power station from coal to biomass in May.
The increased share on a year earlier occurred despite a fall in generation from renewables, and reflects the fact that overall generation was at its lowest quarterly level in the last 16 years.
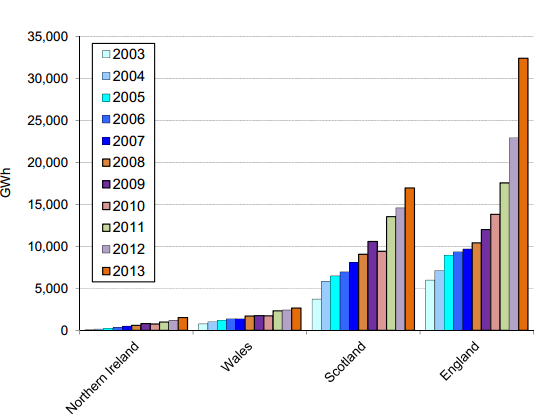
Between 2003 and 2013 there was a 407 per cent increase in generation from renewables in the UK, but faster rates of growth were recorded in Northern Ireland (1,368 per cent), Yorkshire and The Humber (672 per cent), South East (600 per cent), Eastern (511 per cent), North East (483 per cent), East Midlands (463 per cent), North West (416 per cent) and Scotland (356 per cent) (see charts 11 and 12).
For the individual technology groups some of the very large percentage increases are because in 2003 there was very little use of some of the technologies in various regions.
At the same time:
- Share of generation from coal decreased from 34.5 per cent in 2013 Q2 to 28.2 per cent in 2014 Q2.
- Gas’s share of generation increased from 28.7 per cent in 2013 Q2 to 30.2 per cent in 2014 Q2
- Nuclear’s share of generation rose from 18.4 per cent in 2013 Q2 to 22.2 per cent in 2014 Q2.
Renewables share in detail
- Renewables’ share of electricity generation was 16.8 per cent in 2014 Q2, up 0.9 percentage points on the share in 2013 Q2, with the fall in overall generation exceeding that of renewables.
- Renewable electricity generation was 13.2 TWh in 2014 Q2, a fall of 1.0 per cent on the 13.4 TWh in 2013 Q2, and 27 per cent lower than the peak quarterly generation of 2014 Q1 (18.2 TWh).
- Bioenergy generation increased by 8.8 per cent in 2014 Q2, from 5.2 TWh in 2013 Q2 to a record 5.6 TWh, as a result of the recently converted second unit at Drax power station. Solar PV was up 67 per cent, from 0.7 TWh to 1.2 TWh due to increased capacity. Due to very low wind speeds, generation from both onshore and offshore wind fell, by 16.9 per cent and 22.5 per cent, respectively.
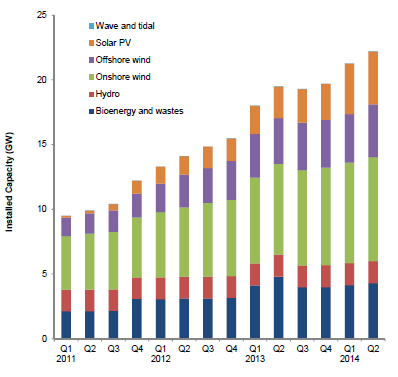
- Renewable electricity capacity was 22.2 GW at the end of 2014 Q2, a 13.8 per cent increase (2.7 GW) on a year earlier, and 4.5 per cent (0.9 GW) increase on the previous quarter, with the Drax conversion being offset by a reduction in capacity at the Ironbridge conversion (following a fire in 2014 Q1).
- By the end of 2014 Q2, 2,816 MW of capacity had been installed, and eligible for, the Feed in Tariff scheme, an increase of 27 per cent on a year earlier, constituting approximately 13 per cent of all renewable installed capacity.
- Liquid biofuels consumption rose by 17.8 per cent, from 394 million litres in 2013 Q2 to a record 464 million litres in 2014 Q2, with biodiesel up by over one third. In 2014 Q2, liquid biofuels represented 4.0 per cent of petrol and diesel consumed in road transport.
The combination of a coherent national strategy for energy savings at home, in business and in all organisations with viable development of renewable energy sources is a double whammy for the UK’s sustainable development over the next few decades. The benefits are compelling enough for a visionary energy savings and generation policy to be formulated in detail.